
 /
/The Internet
The Internet combines advances in information technology (which have greatly increased our capacity for storing and managing information) with advances in communications technology (which allow us to transfer greater amounts of information more easily).
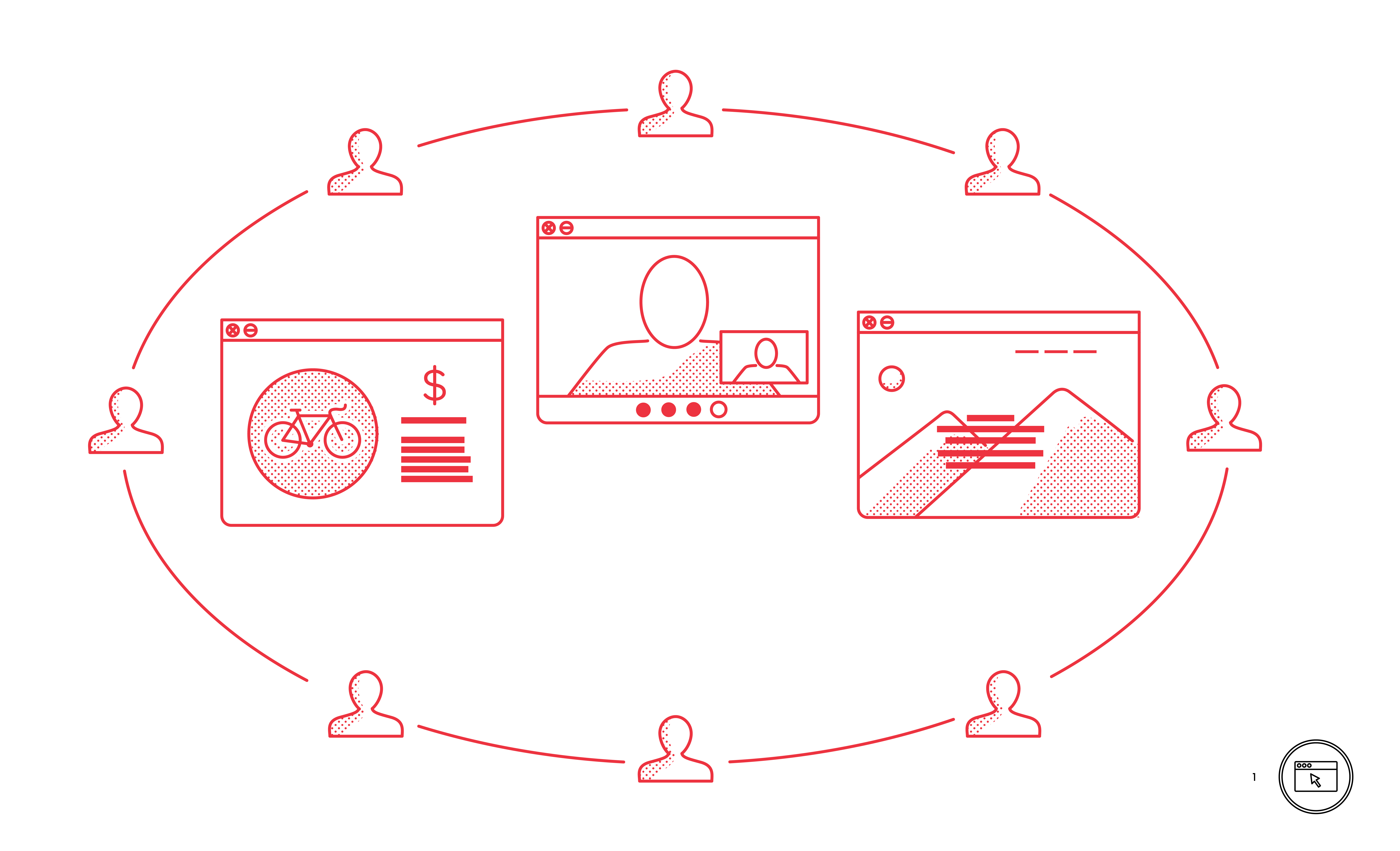 /
/What the Internet is Used for
The Internet connects people and information through services such as email, games, social media, online banking, entertainment and video chat.
 /
/There are Risks on the Internet
The risks on the Internet relate mainly to:
• The difficulty of keeping information private on a technology designed for sharing;
• Knowing whom or what to trust; and
• Proving you are who you say you are.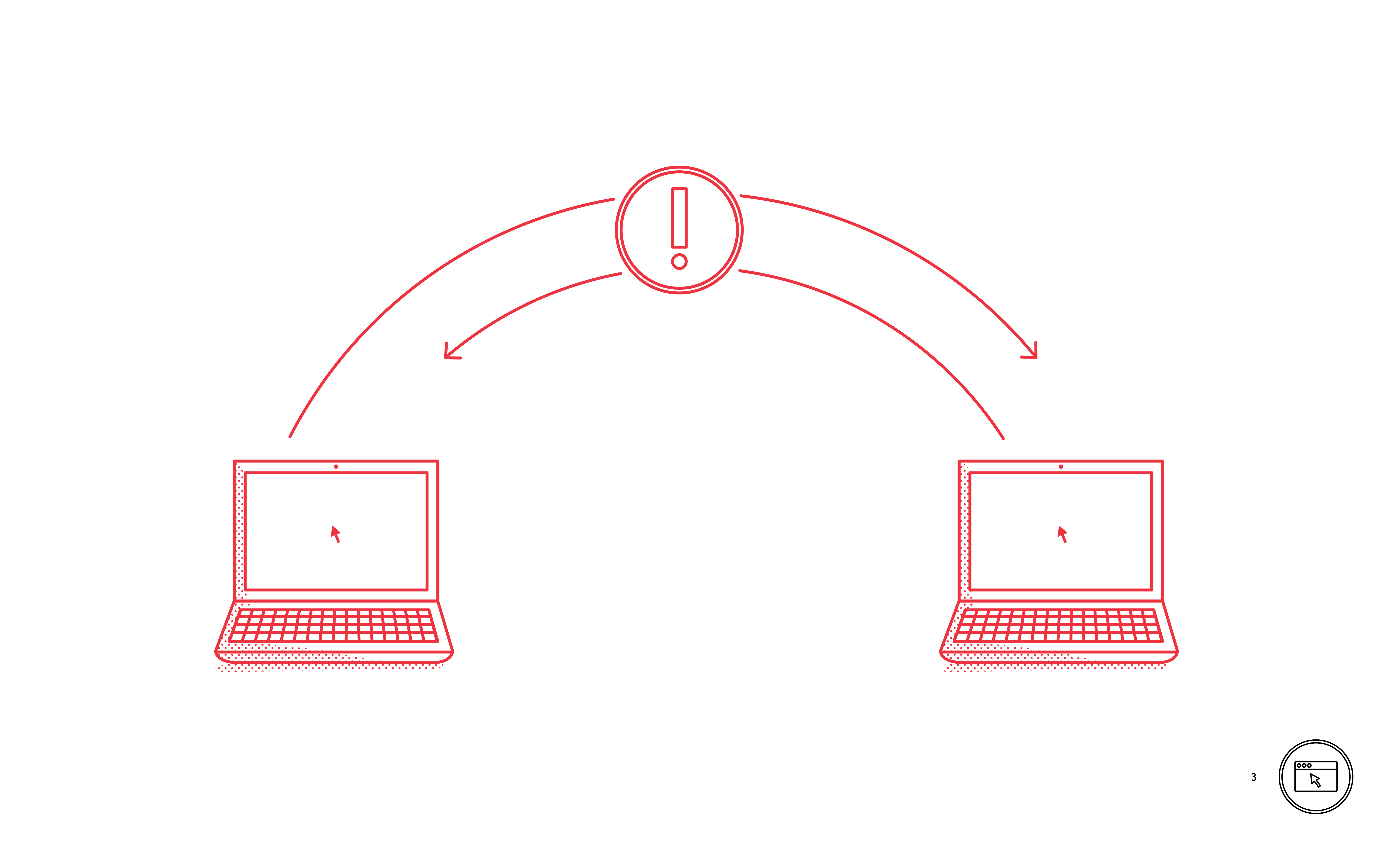 /
/The Internet is Made up of Connected Computers
The Internet is made up of millions of computers linked together to allow information to flow freely between them. The technology used is very trusting. Security is not built into the Internet and should never be assumed.
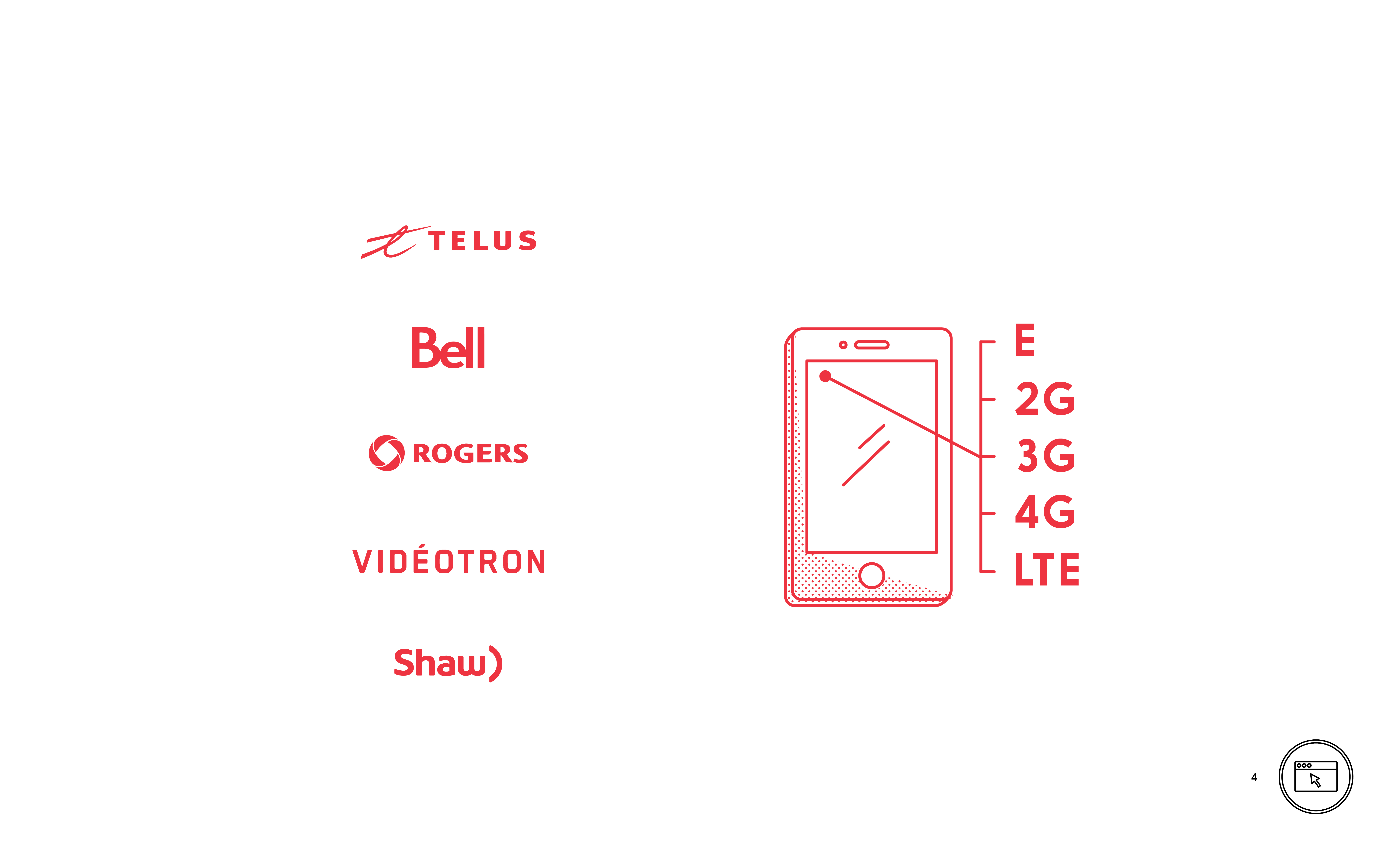 /
/An Internet Service Provider (ISP)
An ISP provides a connection to the Internet. ISPs can provide service to a fixed point, like a home, or to a mobile point, like a cellular telephone. 3rd Generation (3G) and later mobile connections offer good service and a level of security.
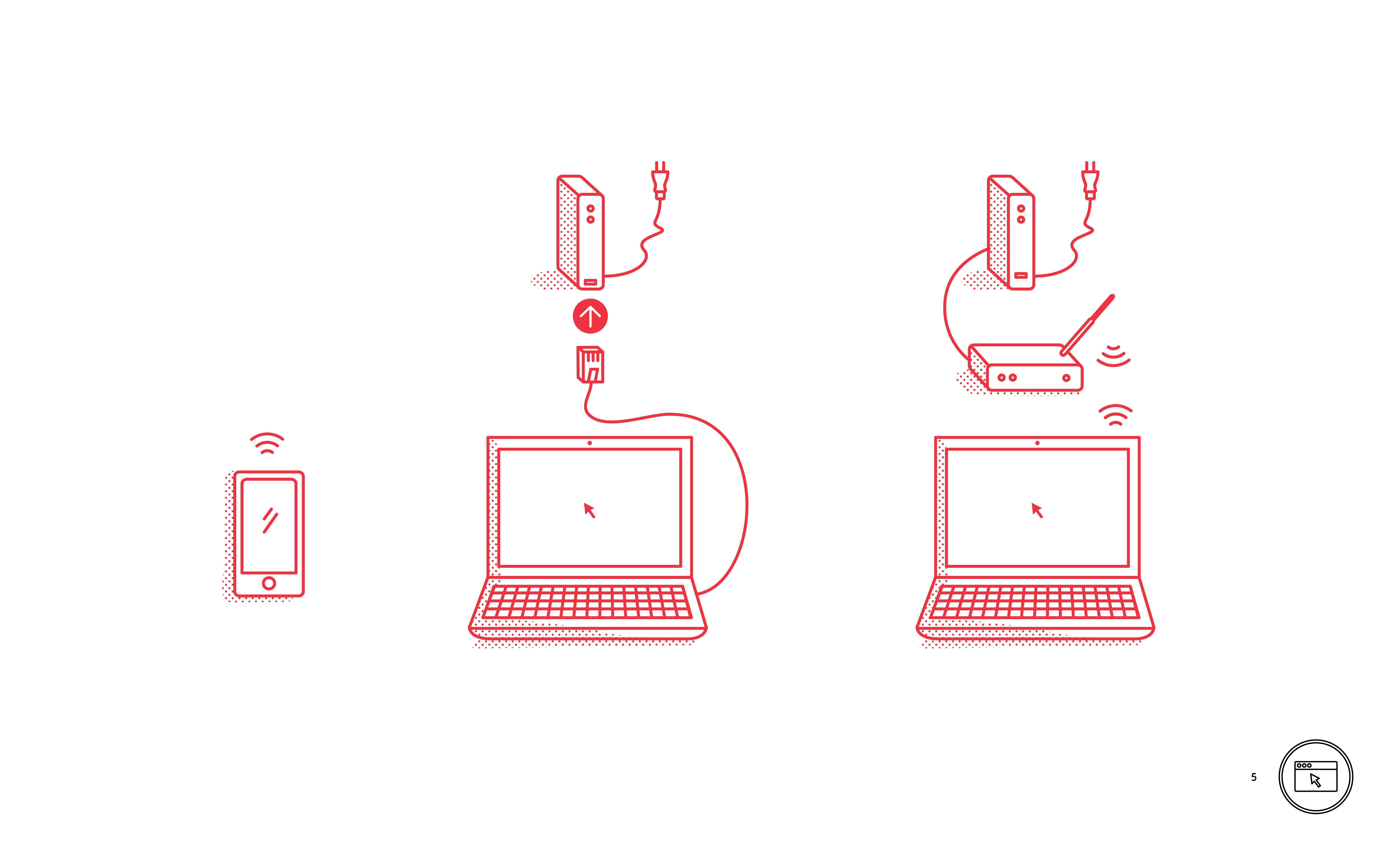 /
/The Internet at Home
Broadband Internet connections allow home networks to access the Internet. Home Internet-enabled devices can connect directly to the Internet router or by Wi-Fi. Ensure Wi-Fi networks are secured with WPA or WP2 and a very strong password.
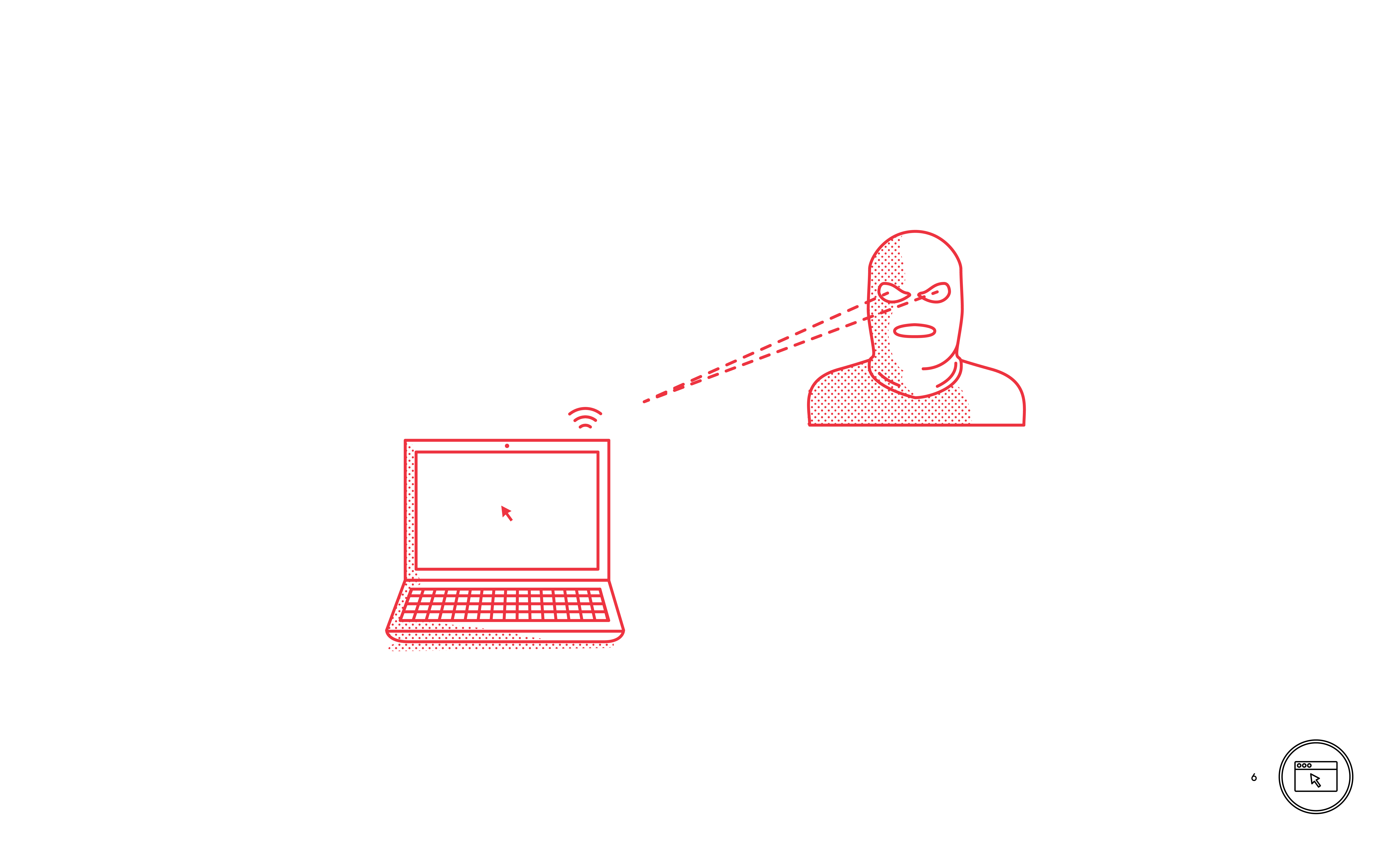 /
/The Internet Outside the Home
Networks outside the home can be less secure than a home network.
Be careful what information you share when connecting to public networks, wherever possible avoid sensitive transactions. /
/The Internet
The Internet connects people and information. Security is not built into the Internet and should never be assumed.
-

Internet Concepts
Let’s see how much you learned about Internet concepts.
Test your knowledge and earn your badge to share
START THE QUIZ
- 1/2
The Internet can be used for:
Email, contacting friends, watching movies or TV shows, checking sports scores
Taking courses, reading books, publishing opinions, sharing photos
Video chat, banking, reading news, research, playing games
All of the above
next question
- 1/2
The Internet can be risky because:
You can only trust websites from big companies
Our usual ways of knowing who we are talking to and who to trust aren’t available
There are more criminals online than there are in the real world
You can waste a whole day watching videos of cute kittens
next question
- 1/2
Information is transferred across the Internet …
In secure channels that ensure privacy
In a series of data packets that can be read by each computer they pass through
In tamper evident packaging for your safety
In a series of data packets that cannot be read by each computer they pass through
next question
- 1/2
An Internet Service Provider (ISP):
Fixes the Internet when it breaks
Is the company that stores the entire Internet
Connects you to the Internet
Is always a telephone company
next question
- 1/2
A Secure Wi-Fi connection:
Has a little yellow shield next to it
Requires a password the first time you connect to it
Has a long name
Stays indoors
next question
- 1/2
A Public Wi-Fi connection:
Is safe if many people use it
Is safe if it requires a password
Is not safe enough to use for sensitive purposes such as banking
Is safe if you wash your hands after using it
next question
-
Internet Concepts
your results
/100Congratulations, you earned your badge!
Share on Facebook
Show the answers
Hide the answers
You are on the right track. Some points need to be clarified. Please review the module and try again.
Restart the quiz
1-The Internet can be used for:
Email, contacting friends, watching movies or TV shows, checking sports scores
Taking courses, reading books, publishing opinions, sharing photos
Video chat, banking, reading news, research, playing games
All of the above
There are many uses of the Internet for communication and processing information.
2-The Internet can be risky because:
You can only trust websites from big companies
Our usual ways of knowing who we are talking to and who to trust aren’t available
There are more criminals online than there are in the real world
You can waste a whole day watching videos of cute kittens
Anything on the Internet can be duplicated or counterfeited so it is very difficult to be sure of whom you are dealing with and how trustworthy they are. Likewise it is difficult for others to be sure that you are authentic as well.
3-Information is transferred across the Internet …
In secure channels that ensure privacy
In a series of data packets that can be read by each computer they pass through
In tamper evident packaging for your safety
In a series of data packets that cannot be read by each computer they pass through
There is no security inherent in the function of the Internet. The system of routing information is very trusting in how it operates and consequently it is important to be aware of extra security features such as encryption.
4-An Internet Service Provider (ISP):
Fixes the Internet when it breaks
Is the company that stores the entire Internet
Connects you to the Internet
Is always a telephone company
An Internet Service Provider connect users to the Internet either over the mobile telephone network or a broadband network to their home.
5-A Secure Wi-Fi connection:
Has a little yellow shield next to it
Requires a password the first time you connect to it
Has a long name
Stays indoors
A Secure WiFi requires that you enter a password the first time that you connect to it. These may be set by the installing technician. An Apple computer will show a little lock next to the network where the network strength is indicated, and on windows computers the network strength indicator will not have a yellow shield next to it.
6-A Public Wi-Fi connection:
Is safe if many people use it
Is safe if it requires a password
Is not safe enough to use for sensitive purposes such as banking
Is safe if you wash your hands after using it
A public Wi-Fi connection is risker than a home connection or a 3G connection to an ISP because there are many people connected to the network. This increases the chance that someone on the network is eavesdropping and increasing the value to criminals of doing so.
Cheat Sheet
What the Internet is used for
The Internet connects people and information through: Email, Games, Social Media, Banking, Entertainment and Video Chat.
DO use the Internet to enrich your life by providing better access to information and an additional way to communicate.
There are risks on the Internet
There are risks on the Internet mainly related to the difficulty with keeping things private on a technology designed for sharing, knowing who or what to trust and being able to prove whom you are.
DO be aware of dangers online and learn to minimize risk.
.
The Internet is made of connected computers
The Internet is millions of computers linked together in a way that allows information to flow freely between them. The technology used is very trusting and there is no security built in to the Internet, it is always something extra.
DO make sure that security has been applied where you are giving or receiving valuable information.
What is an ISP (Internet Service Provider)
An ISP is a service that provides a connection to the Internet. They can provide service to a fixed point, like a home or to a mobile point, like a cellular telephone.
DO look for a 3G, 4G or LTE symbol on your smartphone before using the Internet to ensure a safer connection.
The Internet at home
Broadband Internet connections allow home networks to access the Internet. Wireless home networks (Wi-Fi) should be used with the security features turned on.
DO secure your home Wi-Fi network with a password, using WPA or WP2 as the secure type.
.
The Internet outside the home
Networks outside the home can be less secure than a home network because more people use them. It is important to take extra care when sharing if you are connected to these networks.
DO be careful what information you share when connecting to public networks, wherever possible avoid sensitive transactions. DO use your 3G or 4G connection if you have to send or receive private information outside the home.
Glossary of Terms
3G
The 3rd Generation Mobile telephone standard, capable of supporting telephony, internet access video calls and TV.
4G
The 4rd Generation Mobile telephone standard, capable of supporting web access, gaming, HD TV, video conferencing and other services
ADSL
Asynchronous Digital Subscriber Line is a set of technologies that allow high-speed computer communications over a telephone wire at the same time as a telephone service.
Co-axial Cable
Co-axial cable is a shielded communications cable that allows the transfer of electric signals over a copper conductor.
Crowd-sourced
A system of making use of a large group of people to make decisions or perform work through solicited contributions rather than by using traditional employees or suppliers.
Digitization
The conversion of information to a digital form.
DSL
Digital Subscriber Line is a set of technologies that allow for high-speed computer communications over telephone wire.
Email
Electronic mail.
Fibre Optic
Flexible, transparent glass or plastic cable that can transfer light from one end of the cable to the other.
Fixed Wireless
High-speed wireless.
Internet Protocol
The protocol that regulates the transmission of data packets across the Internet.
Internet Service Provider
A company that provides access to the Internet as a service to subscribers.
LTE
Long Term Evolution is a protocol that allows for the provision of 4th generation mobile telephone services with greater efficiency.
Protocol
A set of rules and conventions for the transfer of information between devices.
Router
A device that manages the routing of information between computers and networks.
Social Media
A service designed to provide tools for socialising with others across the Internet.
Transmission Control Protocol
The protocol that regulates the formation and assembly of data packets for transfer across the Internet.
Video Chat
An Internet service that allows persons to chat while seeing each other with simultaneous bidirectional, real-time video feed.
Wi-Fi
A set of wireless computer networking technologies that allow for small networks.
Wi-Fi base station
A device that provides for a Wi-Fi network and often allows connection to a wired network.
Wireless
Sending and receiving electronic signals by using radio waves.
WPA, WPA2
Wi-Fi Protected Access and Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 are two security protocols designed to protect Wi-Fi networks. These protocols were developed to resolve issues in the earlier “Wired Equivalent Privacy” (WEP) security protocol.
References and Additional Resources
Download SERENE-RISC printable material
Trainers
Trainer Resource – Internet Concepts (PDF)
Lesson Plan – Internet Concepts (PDF)
Lesson Script – Internet Concepts (PDF)
Handout Sheet Answer Key – Internet Concepts (PDF)
Resource Sheet – Internet Concepts (PDF)
Students
Cheat Sheet – Internet Concepts (PDF)
Handout Sheet – Internet Concepts (PDF)
Handout Sheet Answer Key – Internet Concepts (PDF)
Resource Sheet – Internet Concepts (PDF)
Download all the materials for the module “Internet Concepts” (PDF)
Additional resources
External Links
Canadian Internet Statistics
https://cira.ca/factbook/2014/the-canadian-internet.html
The History of the Internet
The OSI Model
Books
How the Internet Works by Preston Galla
2006, Que Publishing
ISBN: 978-0789736260
The Future of the Internet and How to Stop it by Jonathan Zittrain
2000, Yale University Press
ISBN: 978-0300151244
Tubes: A journey to the Center of the Internet by Andrew Blum
2012, Harper Collins Publishers
ISBN: 978-0061994951
Using the Internet for the Over 50s by Greg Holden
2010, Pearson Education Limited
ISBN: 978-0-273-73493-2